Feudalism vs Capitalism
Understanding the distinctions between feudalism and capitalism is intriguing to many, as feudalism is the precursor to capitalism. Feudalism was the societal structure in medieval Europe, characterized by nobles who held land rights and provided military service to monarchs. This system had peasants and landless individuals working as tenants for the nobles who protected them. Over time, another political and economic system emerged, which is now the foundation for most of the western world. This system also allocates control of assets and resources to a select few in society, similar to feudalism. Despite the similarities, there are many differences that will be highlighted in this article.
What is Feudalism?
Those unfamiliar with the concept of feudalism may equate it with a present-day monarchy, where land rights are granted to the nobility. Commoners worked as vassals on the lands of these nobles and received a portion of their produce as sustenance, while the rest belonged to the nobles. The nobles protected the serfs but required them to provide military service to the crown in exchange for land rights. Feudalism was characterized by the principle of exchange, where land rights were held by the nobles in exchange for the military service they provided to kings, while serfs held small pieces of land in return for the service they provided to the nobles. They could keep a portion of the agricultural produce and received protection from landlords in return for their obedience.
Society was divided vertically, with kings at the top, nobility in the middle, and peasants forming the lower classes. Feudalism is all about the relationship and obligations between the king, the lords, and the vassals. Over time, advancements in communication weakened the power of the monarchs, as people disapproved of power being concentrated in the hands of kings. The system of controlling and managing resources changed along with other societal changes, leading to the emergence of capitalism.
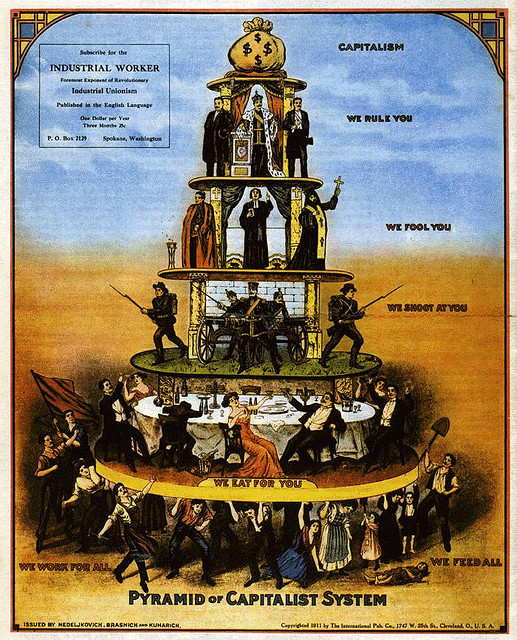
What is Capitalism?
Capitalism’s origins can be traced to a political and social system where the means of production do not remain in the hands of a noble or monarch. A few individuals who invest in machinery and establish factories to employ the working class are called capitalists, and the system is referred to as capitalism. Capitalism is defined by individual rights and, in political terms, is referred to as laissez-faire, meaning freedom. There is a rule of law, and it is a market-driven economy. The means of production and distribution remain in the hands of private individuals rather than the state. The Industrial Revolution created conditions that were conducive to the rise and popularity of capitalism, as wealthy people established industries that attracted people from distant rural areas. Large-scale migration from rural areas to cities began with capitalism.
Key Takeaways
- In feudalism, peasants remain connected to the means of production, whereas in capitalism, workers become alienated from the means of production, which are controlled by capitalists.
- Feudalism is characterized by the principle of exchange, where kings granted land rights to nobles in exchange for military service, and nobles granted protection to peasants in exchange for a portion of the agricultural produce.
- Capitalism is characterized by a free market economy and private ownership.