First Person vs Second Person vs Third Person in English Grammar
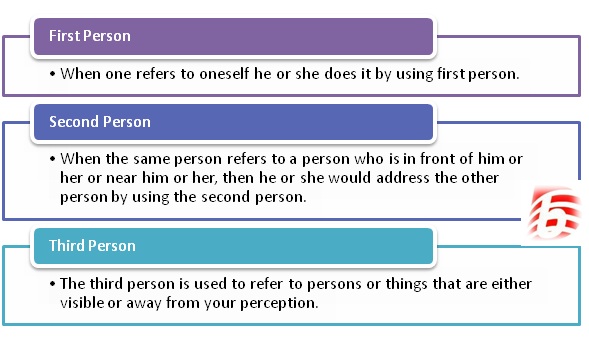
Understanding the distinction between first, second, and third person is crucial when learning English grammar. From a grammatical perspective, these terms refer to personal pronouns. First person refers to ‘I,’ second person refers to ‘you,’ and third person refers to ‘he, she, or it,’ depending on the context. The plural forms of these pronouns are ‘we’ for ‘I,’ ‘you’ for ‘you,’ and ‘they’ for ‘he, she, or it.’
What is First Person?
The first person is reflexive in nature, referring to oneself, as in the sentence: “I went to the office late today.”
What is Second Person?
When addressing someone nearby or in front of them, a person uses the second person, as in: “You know the truth.” It is worth noting that the second person is also used to address the Almighty, even though God is not physically present. Additionally, poets might utilize the second person when addressing inanimate objects, such as: “O Cloud, you should carry my message to my lover soon!”
What is Third Person?
Third person is employed to mention people or things that are either visible or beyond one’s perception. For instance, in the sentence “He knows the reason for my happiness,” the individual referred to by ‘he’ could be near or far from the speaker.
Key Takeaways
- First person (‘I’) refers to oneself, second person (‘you’) addresses someone nearby or in front, and third person (‘he, she, or it’) refers to people or things that are visible or beyond one’s perception.
- Both first and second person have no gender in their application.
- Third person, in contrast, applies to three different genders: masculine, feminine, and neuter, marking a key difference between first, second, and third person.