Micro vs Macro Sociology
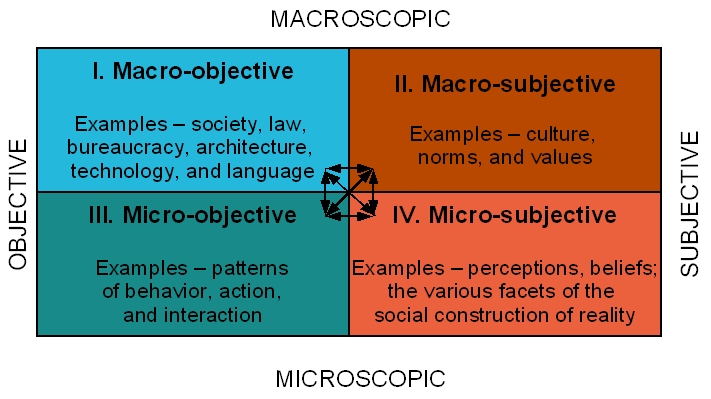
In sociology, there are two major study points: Micro Sociology and Macro Sociology. Micro sociology examines human behavior and social interaction based on small scale studies, while macro sociology focuses on analyzing the social system and population studies on a larger scale. Micro sociology centers around individual face-to-face interactions, whereas macro sociology expands small concepts into broader social processes.
What is Micro Sociology?
Micro sociology is concerned with the study of people in face-to-face interactions, specifically focusing on everyday connections between individuals on a smaller scale. It typically uses interpretive methods to analyze collected data, as it is challenging to use empirical data analysis or statistical methods in micro-sociological studies. The most common research method in this field is symbolic interactions, which involves observing different methods of interactions among individuals to draw conclusions. Subfields such as social psychology and social anthropology can be considered subdivisions of micro sociology. However, micro sociology has its limitations, as it cannot determine the larger forces that may influence individual behavior and interactions.
What is Macro Sociology?
Macro sociology focuses on the social structure on a larger scale, analyzing the social system as a whole and examining the entire population. It delves into broader concepts and can be applied to individuals as well, since individuals and their interactions are part of a larger social system. Macro sociology utilizes statistical analysis and empirical studies to draw conclusions. Although it primarily focuses on broad subject areas, its findings can also be applied to smaller phenomena. Common topics of macro sociology include war, poverty, and social change.
What is the difference between Micro and Macro Sociology?
While both micro and macro sociology are essential subject areas in sociology, there are differences and similarities between them. They both analyze human behavior in society from different angles and can be applied to individual interactions. Key differences include:
- Micro sociology deals with small scale human interactions, while macro sociology focuses on broader social systems and structures.
- Micro sociology uses symbolic interpretation methods in research, while macro sociology relies on statistical and empirical analysis in its findings.
- Micro sociological results cannot be applied to broader concepts, but macro-sociological theories can be applied to the individual level as well.
- Macro sociology is more concerned with broad topics, such as war, gender relations, law, and bureaucracy, whereas micro sociology is primarily interested in topics like family, social status, and individual interactions.