Subject vs Object
Subject and Object are two distinct terms used in the English language with different definitions and roles, particularly in grammar. A sentence generally comprises a subject, verb, and an object. The key to distinguishing a subject from an object is primarily based on the verb.
What is a Subject?
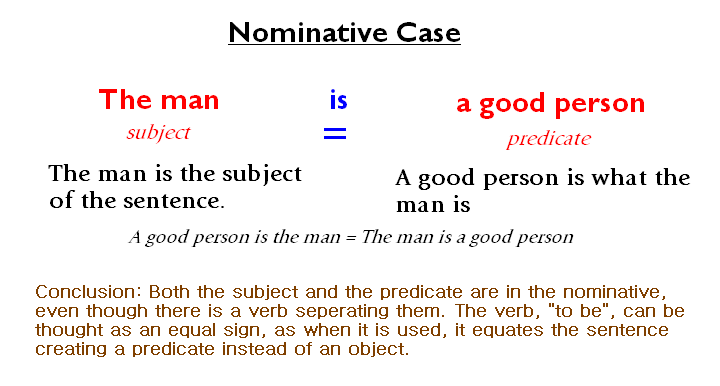
A subject is the reply to the question ‘who’ or ‘what’ placed before a verb. For example, in the sentence “Francis ate a mango,” asking “Who ate a mango?” results in the answer “Francis.” This makes Francis the subject of the sentence. In other words, the subject performs the action, which is represented by a verb. The subject in a sentence is represented by the nominative case, and when a sentence is in active voice, the subject becomes the object in passive voice.
Key Takeaways
- Subjects perform the action in a sentence, while objects are the center of the action.
- Subjects are represented by the nominative case, whereas objects are represented by the accusative case.
- The subject of an active voice sentence becomes the object of a passive voice sentence.
What is an Object?
An object is the reply to the question ‘who’ or ‘what’ placed after a verb. Using the sentence “Francis ate a mango” as an example, asking “Francis ate what?” results in the answer “a mango.” This makes mango the object of the sentence. Objects are the center of the action, which is represented by a verb. While subjects are represented by the nominative case, objects in a sentence are represented by the accusative case. There are two types of objects: direct and indirect. Indirect objects are usually represented by intransitive verbs, whereas direct objects are represented by transitive verbs.
What is the difference between Subject and Object?
- Identifying a subject involves placing ‘who’ or ‘what’ before a verb, while identifying an object involves placing ‘who’ or ‘what’ after a verb.
- Subjects perform the action in a sentence, while objects are the center of the action.
- Subjects are represented by the nominative case, whereas objects are represented by the accusative case.
- The subject of an active voice sentence becomes the object of a passive voice sentence.