What is Dependency Theory?
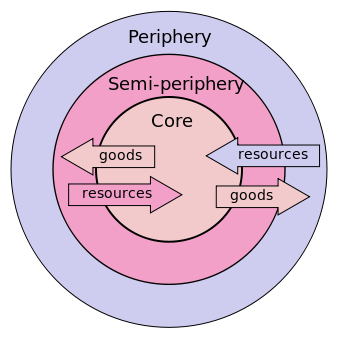
Dependency theory emphasizes that due to colonial and post-colonial endeavors, countries at the periphery (developing countries) are continuously exploited by those at the core (developed or wealthy countries). Dependency theorists argue that the world system is organized in a way that developing countries are always economically dependent and exploited by wealthy countries. They believe that during the colonial period, countries at the core exploited the colonies and developed significantly. For example, most colonial empires exploited various minerals, metals, and other products from their colonies, allowing them to emerge as industrial, wealthy empires. Dependency theorists highlight that if not for such measures, most countries would not have become wealthy empires. They argue that exploitation continues today through neocolonialism, mainly visible through foreign debt and trade.
What is Modernization Theory?
Modernization theory is a development theory that emerged before dependency theory and can be viewed as a reaction to it. Modernization theory describes the transformative processes of societies from underdevelopment to modern societies. It was a key theory used in the 1950s for development and focuses on the processes that transform a society from a pre-modern state to a modern state in terms of economy, politics, society, and culture. The theory emphasizes the importance of education and technology for development. Modernization theory highlights the deficiencies in developing countries, suggesting that they fail to modernize due to such features. However, the theory has limitations, such as failing to recognize that the interests of developed and developing countries are different and that inequality is a key feature that prevents a country from modernizing.
Key Takeaways
- Dependency theory focuses on the exploitation of developing countries by developed countries due to colonial and post-colonial endeavors.
- Modernization theory describes the transformative processes of societies from underdevelopment to modern societies and emphasizes the importance of education and technology for development.
- Dependency theory emerged as a reaction to modernization theory, which has limitations such as not acknowledging the different interests of developed and developing countries and the role of inequality in preventing modernization.