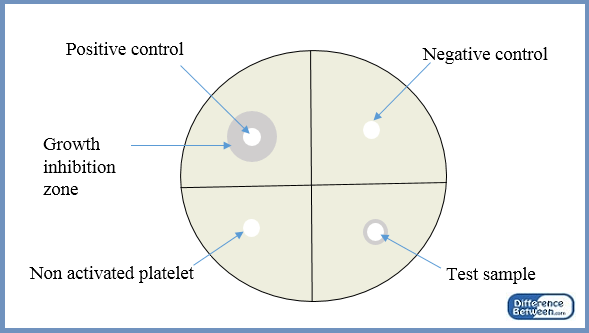
In scientific experiments, controls are essential for obtaining reliable results and increasing the statistical validity of the data set. There are two types of control treatments: positive control and negative control.
Key Takeaways
- Positive control is an experimental treatment that results in the desired effect the researcher expects.
- Negative control is an experimental treatment that does not result in the desired effect of the experimental variable.
- The key difference between the two is that positive control produces a response or desired effect, while negative control produces no response or no desired effect of the experiment.
What is a Positive Control?
A positive control is an experimental control that gives a positive result. It does not have the independent variable being tested but shows the desired effect expected from the independent variable. Positive control is a useful proof to demonstrate that the protocols, reagents, and equipment are functioning well without errors. If experimental errors occur, positive control will not produce the correct outcome, allowing the researcher to identify and optimize the procedure without wasting time, effort, and money.
What is a Negative Control?
A negative control does not give a response to the treatment. In experiments, negative control should be designed in a way that it does not produce the desired outcome of the experiment. If an inhibition is observed in the negative control, it indicates that something is wrong with the experiment.
What is the difference between Positive and Negative Control?
_positive control_ is an experimental treatment performed with a known factor to get the desired effect of the treatment, while _negative control_ is an experimental treatment that does not result in the desired outcome of the experiment. Both types of control are important in an experiment and contribute to the reliability of the experiment.
Summary – Positive vs Negative Control
Controls are essential elements of an experiment, as they help eliminate experimental errors and biases. Results from control experiments are useful for validating statistical analysis of the experiment. The primary difference between positive and negative controls is that positive control shows the expected effect of the treatment, while negative control does not show the effect of the treatment. An experiment with controls is known as a controlled experiment, and positive and negative controls assure that the experiment was done properly and that the outcome is affected by the independent variable.