The key difference between vernacular and colloquial is that vernacular is a language spoken by people living in a particular region or country, while colloquial is a language used in daily life or casual communication. Vernacular is a native language that is sometimes lower in recognition than languages that are considered prestigious. Colloquial language is used by native speakers, and sometimes non-natives find it difficult to translate it. It often consists of slang, idioms and other expressions that are familiar to the native speakers.
Key Takeaways
- Vernacular is a dialect or language used by people living in a specific country or region, often seen as lower in recognition than standard or prestigious languages.
- Colloquial language is used in casual communication and daily conversations, often containing slang, idioms, and other expressions that may be difficult for non-native speakers to understand.
- While both vernacular and colloquial languages are related to regional dialects, vernacular refers to the native language of a region, while colloquial refers to the informal, casual variant of that language.
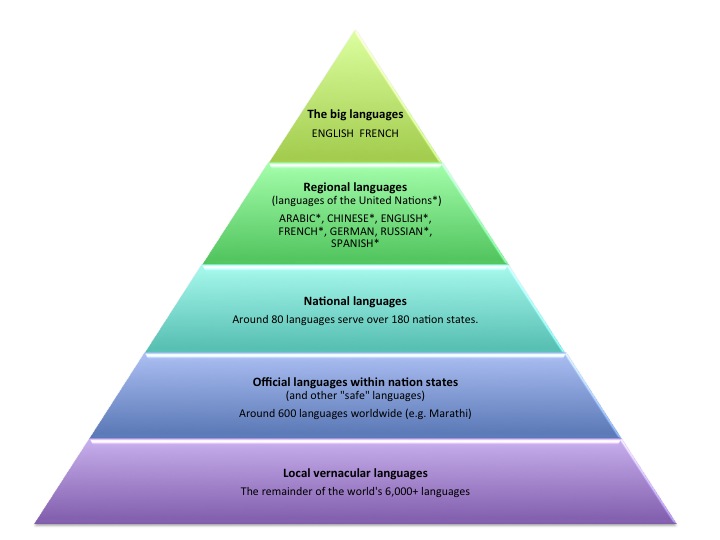
What is Vernacular?
The word vernacular was introduced to English in 1601 by the Latin word ‘vernaculus’, which means ‘national’ and ‘domestic’. Vernacular is a dialect or language used by people living in a specific country or region. It can be identified as a language that has not expanded to a standard variety and can also be recognized as the native language that is spoken in informal situations rather than in writing. Vernacular can be sometimes seen as lower in recognition than the standard language since it is a regional dialect. Therefore, this differs very much from languages that are considered prestigious in society, such as national, liturgical, literary, lingua franca or scientific idioms. Romance languages such as Spanish, Portuguese, French, Italian, Romanian and Catalan all began as vernaculars, and they are also contrasted with lingua franca like Latin.
Examples of Early Vernacular Literature
Divina Commedia – Italian
The Cantar de Mio Cid – Spanish
The Song of Roland– French
Translation of the Bible to Vernacular Languages
Bible in Dutch: published in 1526 by Jacob van Liesvelt;
Bible in French: published in 1528 by Jacques Lefevre d’Étaples
Bible in Spanish: published in Basel in 1569 by Casiodoro de Reina)
Bible in Czech: Bible of Kralice, printed between 1579 and 1593;
Bible in English: King James Bible, published in 1611;
Bible in Slovene, published in 1584 by Jurij Dalmatin.
What is Colloquial?
The word ‘colloquialism’ originated from the Latin word ‘colloquium’, which means ‘conference’ or ‘conversation’. This is a linguistic style used in casual communication. Colloquial language is used in daily conversations and other informal occasions, and it belongs to a local or regional dialect. This variant of language can be recognized as ordinary natural language as well. It is also a non-standard language.
Colloquial language has wide usage of expressive devices and interjections. It is rapidly changing and also consists of incomplete logical formulations and changed syntactic ordering. Slangs are often used by some groups of people in society as a part of their colloquial language. But this happens in some instances only. Colloquial language usually consists of slang, contractions, abbreviations, idioms and also other informal phrases and words that are often known native speakers of a language. Native speakers of a language use colloquial language without realizing it; however, a non-native speaker might find it hard to understand the meaning. This is because colloquial language does not involve the literal usage of words; instead, it is metaphorical or idiomatic.
Examples of Colloquial Language
Contractions
gonna
ain’t
Profanity
Bloody (American English – adjective while British English – curse word)
Regional differences
carbonated drinks – soda, pop, soft drink, Coke (in various regions in America)
truck/lorry, soccer/football, parakeet/budgie (in American English and British English)
Phrases
Penny-pincher
She’ll be right
Pass the buck
Aphorisms
There’s more than one way to skin a cat.
You’re driving me up the wall
I wasn’t born yesterday.
Put your money where your mouth is.
What is the Difference Between Vernacular and Colloquial?
The key difference between vernacular and colloquial is that vernacular is a language spoken by people inhabiting a specific region or country, whereas colloquial is a language used in casual communication or informal situations.
Summary – Vernacular vs Colloquial
Vernacular is a dialect spoken by people living in a specific region or country. It is a language that has not developed to a standard variant and can also be recognized as the native language, which is spoken in informal situations rather than in writing. Colloquial language is used in casual communication, and it belongs to a regional dialect. This is rapidly changing and has wide usage of expressive devices and interjections. Thus, this is the summary of the difference between vernacular and colloquial language.
Reference:
1. “Colloquialism.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 5 July 2021.
2. “Vernacular.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 15 July 2021.
Image Courtesy:1. “The world language hierarchy (adapted from Graddol, 1997)” By Jqho1 – Own work (CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Conversation-dialogue-interview-1262311” (CC0) via Pixabay
Related posts: