Key Takeaways
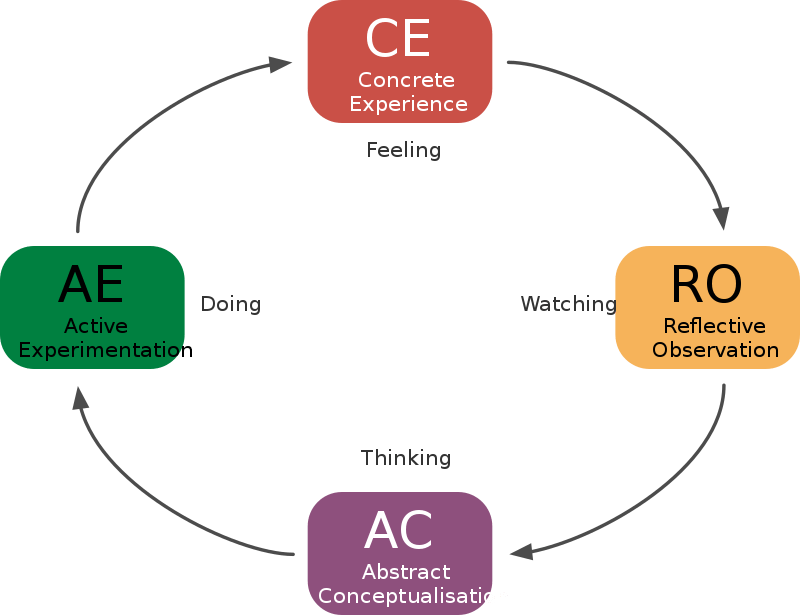
- Kolb’s reflective cycle focuses on the learner’s cognitive process and consists of four stages: concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation.
- Gibbs’ reflective cycle, an improvement on Kolb’s cycle, has six stages: description, feelings, evaluation, analysis, conclusion, and action plan, providing a structured approach to learning from experiences.
- Both reflective cycles are used in learning situations, with Kolb’s cycle aimed at educators for continuous development, while Gibbs’ cycle helps learners understand and improve from their experiences.
What is Kolb’s Reflective Cycle?
Kolb’s reflective cycle, published in 1984 by David Kolb, is a model emphasizing the importance of reflection in the experiential learning cycle. It consists of two sections: a four-stage cycle of learning and four separate learning styles. The cycle of learning includes concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation. The learning styles are diverging, assimilating, converging, and accommodating.
What is Gibbs’ Reflective Cycle?
Gibbs’ reflective cycle, developed by Graham Gibbs in 1988, provides a structured approach to learning from experiences. It includes six stages: description, feelings, evaluation, analysis, conclusion, and action plan. This cycle helps learners examine their experiences, especially those that occur regularly, allowing them to learn and plan from situations that went well or poorly.
What is the Difference Between Kolb and Gibbs Reflective Cycle?
The main difference between Kolb and Gibbs reflective cycles is the number of stages. Kolb’s cycle has four stages: concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation. In contrast, Gibbs’ cycle has six stages: description, feelings, evaluation, analysis, conclusion, and action plan.
Summary – Kolb vs Gibbs Reflective Cycle
Kolb’s reflective cycle is a model that helps structure reflective writing and consists of a four-stage cycle of learning and four separate learning styles. On the other hand, Gibbs’ reflective cycle provides a structured approach to learning from experiences and is an improvement on Kolb’s cycle. Gibbs’ cycle has six stages: description, feelings, evaluation, analysis, conclusion, and action plan. This is the main difference between Kolb and Gibbs reflective cycles.