The main distinction between a noun clause and a noun phrase is that a noun clause contains a subject and a verb, while a noun phrase only includes a noun without a verb. Both noun clauses and noun phrases serve the same grammatical functions as regular nouns, performing as subjects, objects, and complements within a sentence. The primary difference between the two lies in their composition.
Key Takeaways
- A noun clause consists of a noun and a verb and cannot stand alone as a complete thought in a sentence, while a noun phrase consists of a noun and its modifiers, but does not include a verb.
- Both noun clauses and noun phrases can function as subjects, objects, and complements within a sentence.
- The main difference between noun clauses and noun phrases is their structure: noun clauses include a verb, whereas noun phrases do not.
What is a Noun Clause?
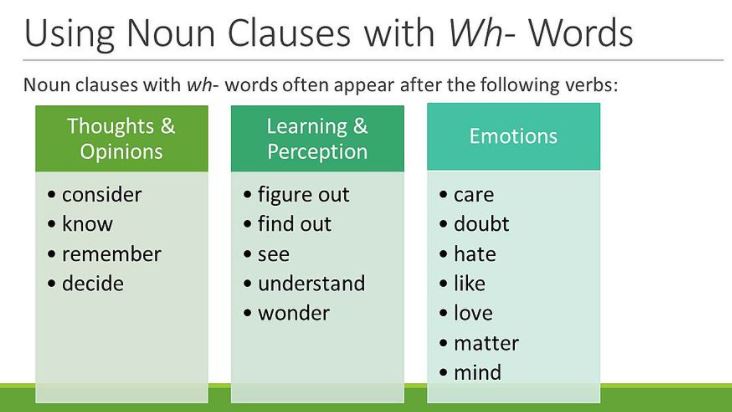
A noun clause is made up of a noun and a verb, similar to a sentence. However, in a sentence, a noun clause cannot stand alone as a complete thought since it is a dependent clause. A noun clause can replace any noun in a sentence, whether it is a subject, an object, or a subject complement. For example, in the sentence “She loves what she wears,” the noun clause “what she wears” is used as the object of the sentence.
Noun clauses can serve various functions in a sentence. They can function not only as objects but also as subjects, direct objects, indirect objects, objects of the preposition, and subject complements. A noun clause can be replaced by a pronoun, such as in the sentence “Did you hear what teacher said,” where the noun clause “what teacher said” can be replaced with the pronoun “it” as in “Did you hear it?”
What is a Noun Phrase?
A noun phrase consists of a group of words headed by a noun, but it does not contain any verbs. A noun phrase serves the role of a noun, and the modifiers of the noun phrase can appear before or after the modifier. For example, in the noun phrase “the girl,” the modifier “the” comes before the head noun “girl.” However, in the noun phrase “the cat on the chair,” the modifier “on the chair” comes before the head noun “cat.”
Noun phrases provide additional details about a noun. In the sentence “The cat on the table drinks milk,” the noun phrase “The cat on the table” functions as the subject of the sentence. Like any other noun, noun phrases also function as subjects, objects, complements, propositional objects, and as prepositional phrases in a sentence. A noun phrase cannot stand alone as a sentence because it does not convey a complete message or meaning.
What is the Difference Between Noun Clause and Noun Phrase?
The key difference between a noun clause and a noun phrase is that a noun clause includes a verb, while a noun phrase does not. A noun clause has a subject and a verb like a sentence, but it is dependent and cannot stand alone as a complete sentence. Conversely, a noun phrase lacks a verb and only contains a noun and its modifiers.
Summary – Noun Clause vs Noun Phrase
The main difference between noun clauses and noun phrases lies in their structure. A noun clause contains a noun and a verb, while a noun phrase does not have a verb and only includes a noun and its modifiers. Both noun clauses and noun phrases serve the same grammatical functions.