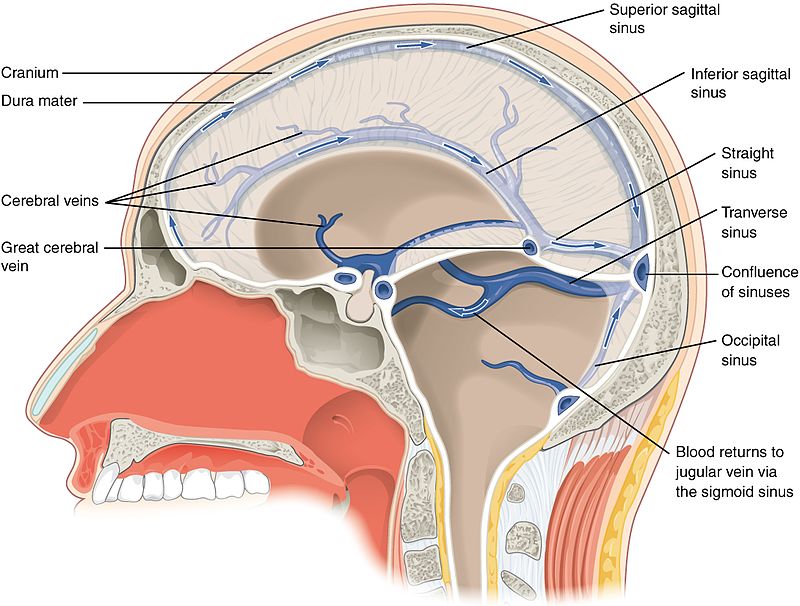
The brain and spinal cord are protected by three layers of membranes called the meninges, which include the dura mater, arachnoid membrane, and pia mater. The dura mater is the outermost layer and is divided into two types: cranial dura, which covers the brain, and spinal dura, which covers the spinal cord.
Key Takeaways
- Cranial dura is the outer meninges that cover the brain, while spinal dura is the outer meninges that cover the spinal cord.
- The cranial dura consists of epidural space and folds and reflections, while the spinal dura does not.
- The function of the cranial dura is to protect the brain, whereas the function of the spinal dura is to protect the spinal cord.
What is Cranial Dura?
The cranial dura mater is the outer meningeal layer, consisting of irregular connective tissues and composed of two layers: the superficial periosteal cranial dura and the meningeal dura. The periosteal dura is closely attached to the internal surface of the skull bones, providing a tubular covering for cranial nerves as they pass through different foramina of the skull. The meningeal dura is continuous with the spinal dura that lies superficial to the arachnoid mater, a dense fibrous membrane that passes through the foramen magnum. The cranial dura folds limit the rotational displacement of the brain and include falx cerebri, falx cerebelli, tentorium cerebelli, and diaphragm sellae.
What is Spinal Dura?
Spinal dura is the outermost layer of the tissue that surrounds the spinal cord, consisting of the endosteal layer and meningeal layer. It primarily consists of a fibrous and non-adherent layer, which comes from the outermost layer of the meninges. The fibrous and elastic bands run parallel to each other and are internally covered by the mesothelium. The blood supply to the spinal dura originates from the anterior and posterior radicular arteries. The main function of the spinal dura is to encase the spinal cord along its length and to partition the central and peripheral nervous systems. Damage to the dura mater occurs mostly during traumatic incidents to the spinal cord during accidents, surgical procedures, meningeal diseases, and lumbar functions, and these damages will not heal by themselves, requiring extensive surgical procedures.
What are the Similarities Between Cranial Dura and Spinal Dura?
Both cranial and spinal dura are meninges, consisting of the dura mater and providing protection to their respective areas. They are prone to traumatic damage more often and are the outermost covering layer of the respective site.
What is the Difference Between Cranial Dura and Spinal Dura?
The key difference between cranial dura and spinal dura is that cranial dura covers the brain while spinal dura covers the spinal cord. Furthermore, the cranial dura consists of epidural space and folds and reflections, while the spinal dura does not. The function of the cranial dura is to protect the brain, whereas the function of the spinal dura is to protect the spinal cord.
Summary – Cranial Dura vs Spinal Dura
In summary, the difference between cranial dura and spinal dura lies in their location and function. Cranial dura is the outer meninges that cover the brain, while spinal dura is the outer meninges that cover the spinal cord. The cranial dura protects the brain, while the spinal dura protects the spinal cord.