The key difference between noun clause and adjective clause is that a noun clause consists of a subject and a verb, whereas an adjective clause consists of a group of words used to modify nouns. A clause is a group of words that contains a subject and predicate. There are different types of clauses, and noun clauses and adjective clauses are two such types. Both of these clauses are dependent clauses and cannot stand alone.
Key Takeaways
- Noun clauses consist of a noun and a verb, while adjective clauses consist of a group of words that modify nouns.
- Both noun clauses and adjective clauses are dependent clauses and cannot stand alone in a sentence.
- Noun clauses function as the subject, object, or subject complement of a sentence, while adjective clauses function as an adjective and modify a noun.
What is a Noun Clause?
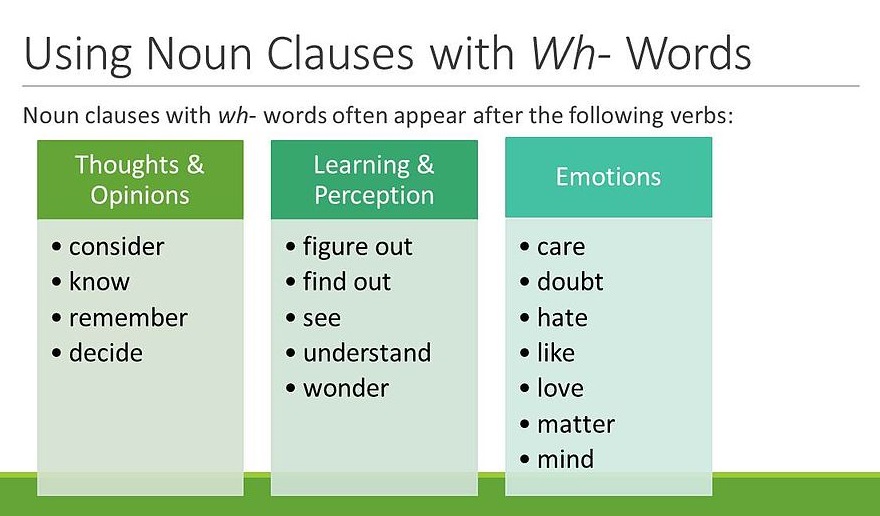
Generally, a noun clause is made up of a noun and a verb. Noun clauses are dependent. Thus, they do not convey a meaningful idea. A noun clause takes the place of a noun in a sentence. It can function as a subject, an object (direct object, indirect object, object of the preposition, etc.), or a subject complement in a sentence.
Since noun clauses are dependent, they are not considered a complete thought in a sentence. Study the following sentences to understand the nature of noun clauses:
She does what she wants.
Whatever you want is fine with me.
In the first sentence, the noun clause functions as the object of the sentence, while in the second sentence, the noun clause functions as the subject of the sentence.
Like nouns are replaced with pronouns, noun clauses can also be replaced with pronouns. For example, in the sentence “Did you buy what you like?”, the noun clause “what you like” can be replaced with the pronoun “it” as “Did you buy it?”
What is an Adjective Clause?
Adjective clauses are made up of a group of words and are used to modify nouns or pronouns. Adjective clauses are dependent clauses, and they follow the noun they modify. For example, in the sentence, “the thief who stole my bag was arrested yesterday,” the clause “who stole my bag” modifies the noun “the thief.”
One main feature that can be seen in adjective clauses is that adjectives clauses always begin with relative pronouns such as that, which, who, whom, and whose or relative adverbs like where, when, and why. These relative pronouns connect the noun and the adjective clause together. Adjective clauses also contain a subject and a verb. They directly give more details and information about the noun.
There are some cases where the relative pronoun can be omitted. For example, “the frock that you bought was beautiful” can be written as “the frock you bought was beautiful” by omitting the relative pronoun. In adjective clauses, details that are not so important about the nouns are presented using a comma. For example, “Ice cream, which many of us adore, has no nutritional value.” The comma in the adjective clauses is used according to necessity.
What is the Difference Between Noun Clause and Adjective Clause?
The key difference between noun clause and adjectives clause is that a noun clause consists of a noun and a verb, whereas an adjective clause consists of a group of words. Moreover, the adjective clauses modify nouns, but the noun clauses do not modify nouns. Besides, both noun clauses and adjective clauses are dependent clauses. Butt, noun clauses start with words such as how, that, what, whatever, when, where, whether, which, whichever, who, whoever, whom, whomever, and why, whereas adjective clauses begin with relative pronouns and adverbs such as that, which, whom whose, where, when, and why. Furthermore, although noun clauses function as the subject, object, or subject complement of a sentence, adjective clause functions as an adjective and modifies a noun.
Summary – Noun Clause vs Adjective Clause
The key difference between noun clause and adjective clause is that a noun clause contains a subject and a verb and whereas an adjective clause consists of a group of words that modify nouns. Moreover, noun clauses function as the subject, object, or subject complement of a sentence, while adjective clause functions as an adjective and modifies a noun.