Key Difference – HTST vs UHT Pasteurization Techniques
Pasteurization, invented by Louis Pasteur, is the partial sterilization of a substance, particularly a liquid such as milk, at a temperature and duration of exposure that destroys objectionable organisms without major chemical alteration of the substance. The key difference between HTST and UHT pasteurization techniques is that in HTST Pasteurization, the product is subjected to a much lower temperature (71.7°C) for a longer period (15 seconds) compared to UHT Pasteurization.
Key Takeaways
- HTST pasteurization has a much lower temperature and longer duration compared to UHT pasteurization.
- UHT pasteurization provides a longer shelf life period than HTST pasteurization but may cause more damage to the nutritional value of the food.
- HTST pasteurization is a pasteurization technique while UHT pasteurization is both a pasteurization and sterilization technique.
What is HTST Pasteurization Technique?
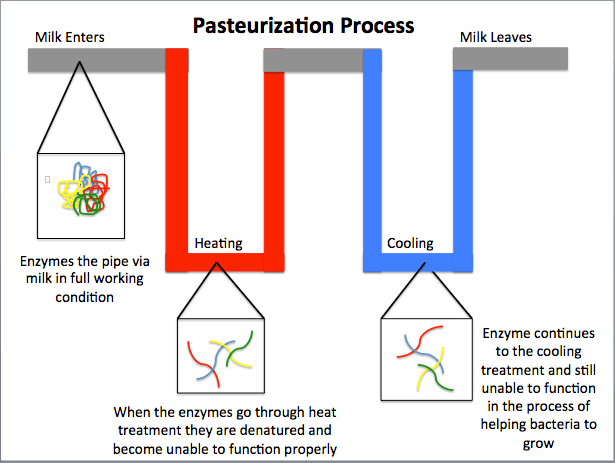
High Temperature, Short Time (HTST) Pasteurization, also known as flash pasteurization, is the most common pasteurization technique in the dairy industry. It is a method of pasteurizing perishable beverages like fruit and vegetable juices, beer, kosher, and wine. Pasteurization makes the product safe for consumption and extends its shelf life compared to unpasteurized products by removing spoilage microorganisms. First introduced in 1993, HTST pasteurization observed a 99.99% reduction of harmful bacteria. This method is faster and more energy-efficient than others, and it maintains the color and flavor of most products. The US standard protocol for milk pasteurization involves subjecting milk to 71.7°C (161 °F) for about 15 seconds to kill Coxiella burnetii (the most heat-resistant pathogen found in raw milk) and most pathogenic bacteria like Salmonella, E.coli, and Listeria.
What is UHT Pasteurization Technique?
Ultra-High-Temperature (UHT) Pasteurization typically involves heating milk or cream to 140 °C (284 °F) for 4 seconds. The milk is then packaged in sterile hermetically-sealed containers, allowing it to be stored for up to 90 days without refrigeration. UHT is commonly used in milk pasteurization but can also be used for fruit juices, cream, soy milk, yogurt, wine, soups, honey, and stews. UHT milk was first used in 1960.
What is the difference between HTST and UHT Pasteurization Techniques?
Temperature, duration, and shelf life are the main differences between HTST and UHT pasteurization techniques. HTST pasteurization occurs at a lower temperature (71.7°C) and longer duration than UHT pasteurization, which occurs at a higher temperature (140°C) for just a few seconds. The shelf life of products pasteurized with the HTST method is 2-3 weeks, while UHT pasteurization provides a longer shelf life of 2-3 months.
HTST pasteurization causes minimal damage to the nutritional value of the food, while UHT pasteurization may kill most of its nutritional value. HTST pasteurization is a pasteurization technique, whereas UHT pasteurization is both a pasteurization and sterilization technique. The HTST technique preserves the color and flavor of the food without causing Millard browning, while the UHT technique may not preserve the color and flavor as it causes Millar browning. HTST pasteurization does not cause protein denaturation, while UHT pasteurization causes structural damage to the protein structure, causing it to elongate. HTST pasteurization kills many pathogenic bacteria, but some nonpathogenic bacteria may remain and cause milk spoilage, while UHT pasteurization kills all bacteria in the milk. In the HTST process, milk is fed into the plant, while in the UHT technique milk is sprayed into the chamber through nozzles.