Plagiarism vs Copyright Infringement
The distinction between copyright infringement and plagiarism lies in the core concept of each term. Both copyright infringement and plagiarism are significant concepts relating to artistic, literary, dramatic, and other types of works. With the rapid advancement of technology and the widespread use of the internet, the importance of understanding these terms is greater than ever. Though they may seem similar and are sometimes used interchangeably, they differ in meaning and consequences.
What is Copyright Infringement?
Copyright is a form of protection or exclusive right provided to creators or owners of intellectual property. It safeguards the expression of an individual’s idea. Infringement refers to the violation of a particular rule, law, or right. Hence, copyright infringement is the violation of the exclusive right given to the owner of a specific work. This violation typically involves the unauthorized or prohibited use of intellectual property, such as literature, music, videos, photos, computer software, and other original works. In short, the owner’s permission or consent was not obtained before using the work.
For a claim of copyright infringement to be valid, the work must be protected by copyright. Copyright allows the owner of a creative work to reproduce, distribute, display, perform, or create derivative works based on their creation. Therefore, copyright infringement occurs when another person or organization exercises these rights without the owner’s permission. Copyright infringement often takes place in the entertainment industry, particularly in music and films.
A recent example of copyright infringement is the claim that Pharrell Williams’ song “Happy” is a reproduction or derivative work of a song by Marvin Gaye. Copyright infringement is proven through circumstantial evidence, which must show a substantial similarity between the original work and the copy and that the person copying had access to the original work. If each work was created independently, then despite their similarity, it does not constitute infringement. Copyright infringement can result in legal consequences, including injunctions and damages.
What is Plagiarism?
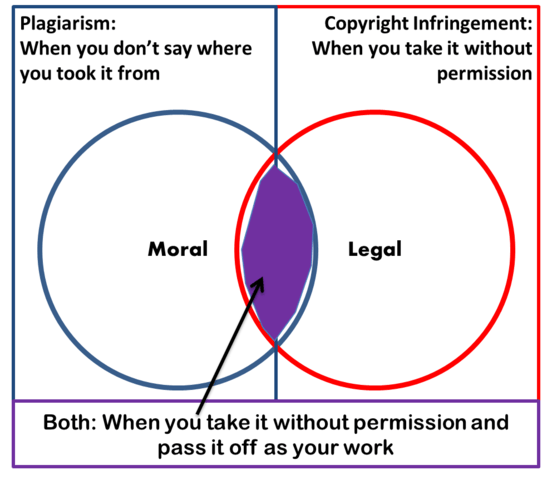
Plagiarism refers to the theft or appropriation of another person’s literary creation and presenting it as one’s own work. Literary work encompasses various forms, such as ideas, book excerpts, research papers, theses, articles, poems, and similar works. In simple terms, it means taking credit for another person’s writing. Students, journalists, writers, and academics are familiar with the term plagiarism. The internet has become a popular source for people to steal, extract, and use others’ literary works as their own. Plagiarism is not a legal concept like copyright infringement but instead focuses on an individual’s morals and ethics.
The simple function of ‘copy-paste’ has been misused and abused by many people to reproduce someone else’s work as their own without giving the original author any credit. To combat plagiarism, schools, universities, and other institutions have implemented rules and regulations regarding the reproduction or extraction of another person’s work. Proper formatting styles, references, bibliographies, citations, and footnotes play a vital role in ensuring that plagiarism is avoided. Those found guilty of plagiarism face severe penalties, such as receiving zero marks on assignments, suspension from school, or even expulsion.
Plagiarism is a form of misrepresentation, where a person falsely or fraudulently claims the work as their own creation. A person guilty of plagiarism is considered dishonest and lacking essential morals, such as integrity. While plagiarism is not a crime, it has consequences, as it severely damages a person’s reputation and credibility and undermines their ability. Examples of plagiarism include quoting someone else’s idea without acknowledging them or using quotation marks, reproducing passages from a literary work without proper citation or references, and paraphrasing someone else’s ideas without giving credit. Plagiarism differs from copyright infringement because it covers even material not protected by copyright.
Key Takeaways
- Copyright infringement refers to a violation of the exclusive right granted to the owner of a specific work, while plagiarism is the theft or appropriation of another person’s literary creation and presenting it as one’s own work.
- Copyright infringement is a legal concept and crime, whereas plagiarism is not a legal concept and focuses on an individual’s morals and ethics.
- To establish a claim of copyright infringement, the work must be protected by copyright, while plagiarism covers even material that is not protected by copyright.