The primary distinction between voice and speech in grammar is that voice indicates whether a verb is active or passive, while speech refers to how we represent the speech of others or ourselves. Speech in grammar has two main categories: direct speech and indirect speech. Voice in grammar also has two main categories: active voice and passive voice. These two categories in grammar can be confusing and challenging for language learners.
Key Takeaways
- Voice in grammar determines if a verb is active or passive.
- Speech in grammar refers to representing the speech of others or ourselves, divided into direct and indirect speech.
- Both voice and speech have two main categories, which can be confusing for language learners.
What is Voice in Grammar?
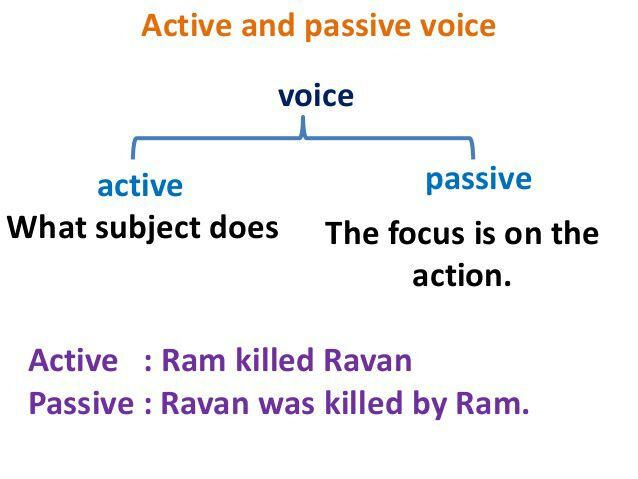
Voice in grammar determines whether a verb is active or passive. A sentence is active when the subject is the doer of the action, while it is passive when the subject is the target or undergoer of the action. Active sentences are considered to be in active voice, and passive sentences are in passive voice.
What is Speech in Grammar?
Speech in grammar refers to how we represent the speech of other people or ourselves. There are two types of speech: direct speech and indirect (reported) speech. Direct speech involves repeating the words of someone directly, while indirect speech involves reporting the words spoken by someone.
What is the Difference Between Voice and Speech in Grammar?
The voice in grammar indicates whether a verb is active or passive, while speech in grammar indicates how we represent the speech of other people or ourselves. This is the key difference between voice and speech in grammar. Furthermore, speech has two main categories as direct speech and indirect speech, while voice also has two main categories as active voice and passive voice.
Summary – Voice vs Speech in Grammar
Direct and indirect speech and active and passive voice are two essential categories in grammar. The key difference between voice and speech in grammar is their function.